
An incoming action potential permits the release of neurotransmitters to propagate the signal to the post synaptic cell. Dendrodendritic synapses are activated in a similar fashion to axodendritic synapses in respects to using a chemical synapse. This is in contrast to the more common axodendritic synapse ( chemical synapse) where the axon sends signals and the dendrite receives them. Neuronal polarity: An evolutionary perspective.Dendrodendritic synapses are connections between the dendrites of two different neurons.
Brain basics: The life and death of a neuron. 35.2: Neurons and glial cells - neurons. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. We link primary sources - including studies, scientific references, and statistics - within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. Multipolar neurons occur throughout the CNS. Each neuron has one axon but multiple dendrites extending from the cell body. Multipolar neurons are the most complex and commonly occurring type of neuron within the human body. Their presence in humans is limited, but they play an important role within the ears, nose, and eyes. Unipolar neurons do not occur in humans.īipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite extending from the cell body. The axon splits up into dendrites at the ends. Unipolar neurons are the simplest form, with one axon extending from the cell body. The arrangement of these components determines the type of neuron. These are the cell body, axons, and dendrites. Other forms, including pseudounipolar and anaxonic neurons, also exist. The three main types of neurons are unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar. Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information around the body, and some types form part of the CNS. However, they do have pseudounipolar neurons. A multipolar neuron only has one axon extending from the cell body, but multiple dendrites grow out of it, making transmitting information easier. A bipolar neuron has two completely independent structures extending from the cell body, one of which is an axon and the other a dendrite. A unipolar neuron has one axon which extends into dendrites, though this splits into two parts in pseudounipolar neurons. These components are called axons, which transmit information, and dendrites, which receive information. The structural components of a neuron determine whether it is unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar. What anatomical characteristics determine whether a neuron is unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar? However, unipolar and bipolar types can also be sensory neurons. 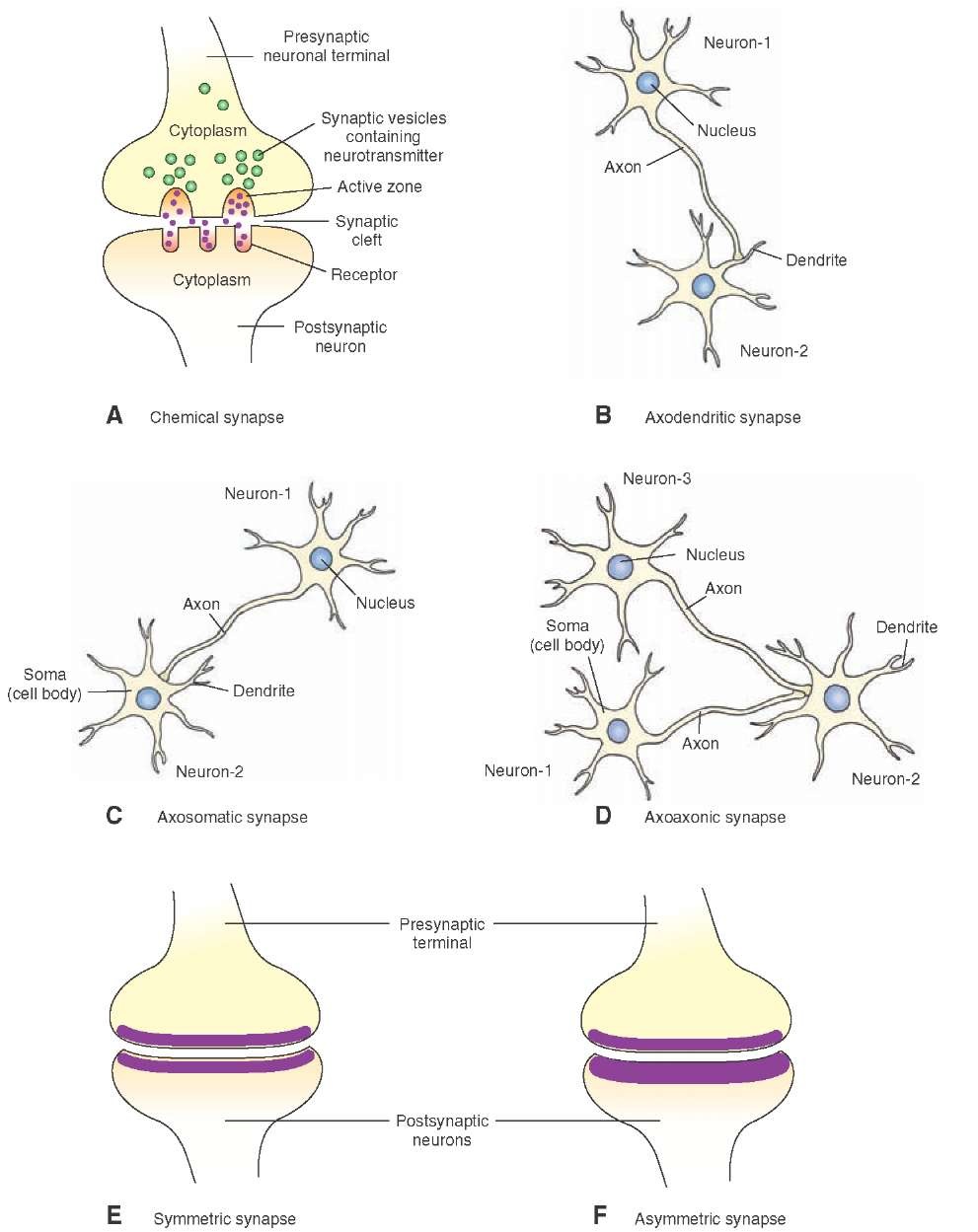
Most of the sensory neurons in a human body are pseudounipolar. Is a sensory neuron unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar? The types include:īelow, we answer some common questions about unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar neurons. Some neurons contain multiple dendrites, while others have none. There are several types of neurons with different structures. These synapses are present at the tips of dendrites. Neurons send information to each other by transmitting chemical signals called neurotransmitters across special junctions called synapses. Dendrite: This part, which looks like the branches of a tree, receives signals for the cell.Axon: This part, which looks like a long tail, transmits signals from the cell.Cell body, o r soma: The cell body has a nucleus that contains the cell’s genetic material and controls the cell’s activities.The components of the neuron work together to facilitate nerve function. The cell structure enables neurons to pass on information, as they have long extensions from the cell body for transmitting and receiving information.

Share on Pinterest koto_feja/Getty ImagesĪ neuron is a nerve cell that passes information around the body through electrical impulses and chemical signals.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
